A Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) helps track tire pressure and alerts you if it’s too low or too high. A Tire Pressure Monitor fault means the system isn’t working correctly, often due to sensor damage, low tire pressure, battery failure, or interference. Ignoring this issue can lead to poor fuel efficiency, uneven tire wear, or even accidents.
Fixes include checking tire pressure, resetting the system, replacing faulty sensors, or updating software. Regular maintenance, careful driving, and protecting sensors from corrosion help prevent problems. In this blog, we will cover TPMS faults in detail, including causes, fixes, and preventive measures to keep your vehicle safe.
You can learn more about Tire Sizes for different vehicles.
What Is a Tire Pressure Monitor Fault?
A tire pressure monitor fault occurs when your vehicle’s TPMS fails to accurately track tire pressure. This malfunction prevents the system from properly monitoring your tires and alerting you to pressure issues, which can compromise your vehicle’s safety and performance.
When detected, your dashboard displays a warning light—typically a horseshoe-shaped icon with an exclamation mark inside. The light may flash initially for 60-90 seconds before turning solid, indicating a persistent system problem rather than just low tire pressure.
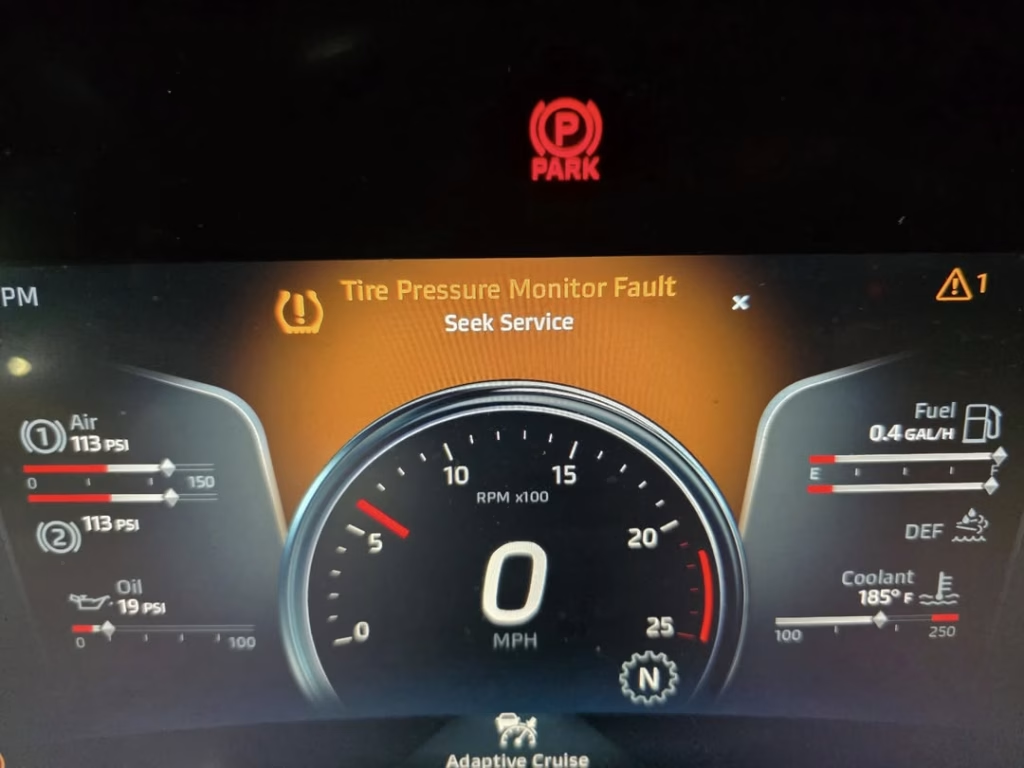
Why It Matters
Studies show that TPMS has reduced underinflated tires by over 55%, preventing countless accidents. When the system fails, you lose this critical safety feature, increasing risks such as higher accident risk, faster tire wear and blowouts, poor fuel efficiency, and expensive repairs to suspension, wheels, and tires.
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms helps you address issues before they compromise safety:
- Persistent TPMS Warning Light: Stays illuminated or flashes even when tires are properly inflated
- Inaccurate Pressure Readings: Displays incorrect pressure levels or inconsistent data
- No Data Displayed: One or more tires show no readings, indicating dead sensor batteries
- False Pressure Alerts: Frequent warnings when tires are within recommended range (30-35 PSI)
- Unresponsive System: Fails to update readings when pressure changes
Tire Pressure Monitor Fault Meaning and Purpose
The TPMS constantly monitors your tire pressure and alerts you if it drops below the recommended level. When a problem is detected, you’ll see a warning light on the dashboard. This is your car’s way of telling you to check your tires.
By maintaining the correct tire pressure, TPMS plays a crucial role in:
- Enhancing safety – Properly inflated tires improve traction, stability, and braking performance.
- Increasing fuel efficiency – Underinflated tires create more rolling resistance, making the engine work harder and consuming more fuel.
- Extending tire lifespan – Uneven tire pressure can lead to premature wear, reducing the life of your tires.
Understanding TPMS: Types and Functions
A Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is a built-in safety feature that tracks your vehicle’s tire pressure and alerts you to issues. There are two types used in modern vehicles:
Direct TPMS
Direct TPMS uses individual sensors inside each tire to measure real-time air pressure. These sensors are attached to the valve stem or mounted inside the tire and wirelessly transmit data to the car’s computer.
Advantages: More accurate, provides real-time readings for each tire, detects gradual leaks and temperature changes.
Disadvantages: More expensive to install and replace, sensor batteries wear out over time.
Indirect TPMS
Indirect TPMS relies on your car’s ABS sensors to track wheel speed. If a tire is underinflated, its decreased diameter causes it to rotate faster, triggering the warning light.
Advantages: Less expensive, no extra sensors needed, no batteries to replace.
Disadvantages: Less accurate, needs recalibration after tire maintenance, can give false alerts due to uneven wear.
Most modern vehicles use direct TPMS due to its accuracy and reliability. Check your vehicle’s manual to confirm which system your car uses.
How Does the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Work?
The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is designed to keep an eye on your vehicle’s tire pressure in real time. It helps prevent tire-related issues by alerting you when one or more tires are underinflated or overinflated. But how exactly does it work?

Direct TPMS: Measures Pressure Inside the Tire
Direct TPMS uses pressure sensors inside each tire to track air pressure. These sensors are usually attached to the valve stem or mounted inside the tire. Here’s how it works:
- Each tire has a sensor that measures air pressure and sometimes temperature.
- The sensors wirelessly transmit data to the vehicle’s computer system.
- If the pressure drops below or above the recommended range, the system triggers the TPMS warning light on the dashboard.
Indirect TPMS: Uses ABS Sensors to Detect Pressure Changes
Indirect TPMS doesn’t measure air pressure directly. Instead, it monitors wheel speed through the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) sensors. Here’s how it works:
- When a tire loses air, its diameter decreases, causing it to rotate faster than the other tires.
- The system detects this speed difference and assumes a tire is underinflated.
- It then triggers the TPMS warning light on the dashboard.
Understanding Your Tire Pressure Warning Light
When the TPMS detects a tire pressure issue, it illuminates a warning light on your dashboard. This light typically looks like a horseshoe shape with an exclamation mark (⚠) in the middle.

- Light Stays On – This means a tire has dangerously low air pressure, possibly due to a slow leak or sudden air loss.
- Tire Pressure Sensor Fault Flashing and Then Turns Off – This usually indicates a problem with the TPMS system itself, meaning the sensors may not be working properly.
Understanding how TPMS works can help you prevent tire-related issues, improve fuel efficiency, and ensure a safer driving experience.
Common Causes of TPMS Faults
A TPMS fault occurs when the system is unable to correctly monitor tire pressure. While some issues are minor and easy to fix, others may require professional repair. Below are the most common causes of TPMS malfunctions.

1. Low Tire Pressure
The most common trigger for TPMS warnings. Caused by punctures, temperature changes (cold weather contracts air), or gradual air loss. Always check and inflate tires to recommended pressure first.
2. Sensor Damage
Delicate sensors can be damaged during tire changes, by potholes, curbs, or sharp objects like nails. Impact damage often requires sensor replacement.
3. Sensor Battery Failure
TPMS sensors run on lithium batteries lasting 5-10 years (average 7 years) or 60,000-100,000 miles. Lifespan varies based on driving patterns—stop-and-go traffic drains batteries faster than highway driving. Temperature extremes also affect longevity. Batteries are sealed inside sensors, so the entire unit must be replaced when batteries die.
4. Corrosion
Exposure to moisture, road salt, and extreme temperatures causes sensor corrosion over time. Corroded valve stems lead to leaks, sensor failure, or complete detachment. Regular cleaning and corrosion-resistant valve caps help prevent this.
5. Signal Interference
TPMS sensors communicate via radio signals that can be disrupted by electronic devices (dash cams, phone chargers), aftermarket modifications (remote starters), environmental factors (power lines, radio towers), or faulty receiver modules.
6. Software Glitches
Outdated vehicle software may cause inaccurate readings or false warnings, especially after tire replacements or rotations. Software updates or system resets typically resolve these issues.
7. Faulty Wiring
Loose or damaged wires, frayed cables, blown fuses, or faulty TPMS control modules disrupt signal transmission. Professional diagnosis with specialized tools is usually needed.
Diagnosing Tire Pressure Monitor Faults
If your TPMS warning light turns on, it’s important to diagnose the issue before assuming it’s a sensor failure. Here are a few key steps to identify the root cause of the problem.
Manual Tire Pressure Check
Start by checking tire pressure with a reliable gauge. Locate recommended pressure in your manual or on the driver’s side door jamb. Measure each tire when cold and inflate to proper levels. If the light turns off after driving a few miles, low pressure was the issue.
Visual Inspection
Check valve stems for cracks, bends, or corrosion. Look for sensor damage and inspect tires for punctures or leaks. Remove any debris around sensor areas.
Diagnostic Tools
Use an OBD-II scanner to check for stored error codes, a TPMS scan tool to read sensor IDs, check battery status, and measure signal strength, or a TPMS relearn tool for recalibration after sensor replacement. Professional diagnostic tools pinpoint exact causes—damaged sensors, dead batteries, software issues, or communication problems.
How to Fix Tire Pressure Sensor Fault?
Once you’ve diagnosed the issue, the next step is fixing the TPMS fault. Some solutions are simple, like adjusting tire pressure, while others may require sensor replacement or professional repairs.
1. Adjust Tire Pressure
One of the most common causes of a TPMS fault is low or high tire pressure. Follow these steps:
- Check tire pressure using a gauge.
- Inflate or deflate tires to match the recommended pressure (found in the owner’s manual or driver’s side door jamb).
- Drive for a few minutes. In many vehicles, the TPMS light will turn off automatically after correcting the pressure.
If the light remains on, additional troubleshooting is needed.

2. Resetting the TPMS
After adjusting the pressure, you may need to reset the TPMS system manually. The method varies by vehicle, but common steps include:
- Using the TPMS reset button (if available). Usually located under the dashboard or in the glove box.
- Holding the button until the TPMS light blinks, then drive for a few miles to allow recalibration.
- Using the vehicle’s infotainment system. Some modern cars have a TPMS reset option in their menu.
Refer to your owner’s manual for the exact reset procedure.
3. Tire Pressure Monitor Fault Sensor Replacement
If a TPMS sensor is damaged or its battery has died (typically lasting 5-10 years), it must be replaced.
- Check for sensor failure using a TPMS scan tool or OBD-II scanner.
- Purchase a compatible replacement sensor (OEM or high-quality aftermarket).
- Install the new sensor and perform a TPMS relearn process to sync it with the system.
Since TPMS sensors are mounted inside the tire, professional installation may be necessary.
4. Addressing Corrosion
Corrosion can interfere with TPMS performance, especially in areas with harsh weather conditions.
- Check valve stems and sensor housings for rust or corrosion.
- Clean minor corrosion with a wire brush or rust remover.
- Replace heavily corroded components to prevent leaks and sensor failure.
5. Resolving Signal Interference
Radio signals from wireless devices, power lines, or other vehicle systems can disrupt TPMS communication.
- Turn off or relocate nearby electronic devices that could be causing interference.
- Drive away from high-interference areas (like power plants or dense city centers) to see if the TPMS light turns off.
- Check for aftermarket electronics—some modifications, like remote starters, can interfere with TPMS signals.
6. Software Updates
A software glitch may cause false TPMS warnings, even when the sensors and pressure are fine.
- Check for manufacturer recalls or software updates.
- Visit a dealership or mechanic to ensure your TPMS software is up to date.
7. Repairing Wiring Issues
Faulty wiring can disrupt the TPMS signal, leading to inaccurate readings or system malfunctions.
- Inspect sensor wiring for frayed or disconnected cables.
- Repair or replace damaged wiring to restore communication between the TPMS and the vehicle’s ECU.
To ensure optimal performance, be sure to consult a professional for further advice or visit our Tire Repair page for expert services.
How to Tire Pressure Sensor Fault Reset?
The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) keeps track of your tire pressure and alerts you if a tire is underinflated. After inflating the tires, rotating them, or replacing one, you may need to reset the TPMS to ensure accurate readings. Follow these simple steps to recalibrate the system:
Step 1: Prepare the Vehicle
- Park the car safely and turn on the ignition.
- Ensure all tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure.
Step 2: Access the TPMS Calibration Menu
- Locate the Home button on the left side of the steering wheel.
- Use the selector wheel to navigate to Settings and select it.
- Scroll down to TPMS Calibration and choose this option.
Step 3: Start the Calibration Process
- Select Calibrate and confirm the action.
- A message should appear confirming that calibration has begun.
- If you see Calibration Failed to Start, repeat the steps carefully.
Step 4: Drive to Finalize Calibration
- The system will automatically adjust as you drive.
- After a few miles, the TPMS light should turn off, confirming the reset.
Why Won’t My TPMS Light Turn Off After Resetting?
If your TPMS light remains on even after resetting, it may indicate an issue beyond tire pressure. The system monitors not only air pressure but also weight distribution and imbalances. Several factors can interfere with its readings, causing the light to stay on.
Possible Causes:
- Damaged Tires – Even with proper inflation, worn-out or damaged tires can cause an imbalance, triggering the TPMS light.
- Excess Weight in the Vehicle – Carrying heavy loads in the cabin or trunk can affect tire pressure readings.
- Use of Snow Chains or Towing a Trailer – These can alter the weight distribution, making the sensors detect a false low-pressure condition.
If the TPMS light persists, inspect your tires for damage, remove excess weight, and ensure the system is functioning properly. If the issue continues, a professional inspection may be needed to check for faulty sensors.
TPMS Regulations and Legal Compliance
Ignoring TPMS issues isn’t just a safety risk. It can also lead to legal trouble. Many countries require vehicles to have a functional TPMS to improve road safety. Failure to comply may result in:
- Fines or penalties for non-working sensors.
- Failed vehicle inspections in regions with strict regulations.
- Increased liability if an accident occurs due to neglected tire pressure issues.

Car Brands with Reported TPMS Issues
Several car manufacturers have reported Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) issues across different models. Commonly affected brands include:
- Mercedes-Benz
- BMW
- Toyota
- Ford
- Honda
- Nissan
- Kia
- General Motors (GM)
- Hyundai
- Volkswagen
FAQs
What does a TPMS warning light mean?
It indicates low tire pressure or a fault in the TPMS system.
Can I drive with the TPMS light on?
Yes, but it’s unsafe; check and adjust tire pressure immediately.
How do I reset the TPMS light?
Inflate tires to the correct pressure, then use the TPMS reset button or drive a few miles.
What causes TPMS faults?
Common causes include low tire pressure, sensor damage, battery failure, corrosion, or signal interference.






